Ultraviolet radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that comes primarily from the sun. While it is invisible to the human eye, it has profound effects on our health and the environment. This article will explore the nature of ultraviolet ( UV) radiation, its benefits and risks, and its various applications in different fields.
What is Ultraviolet Radiation?
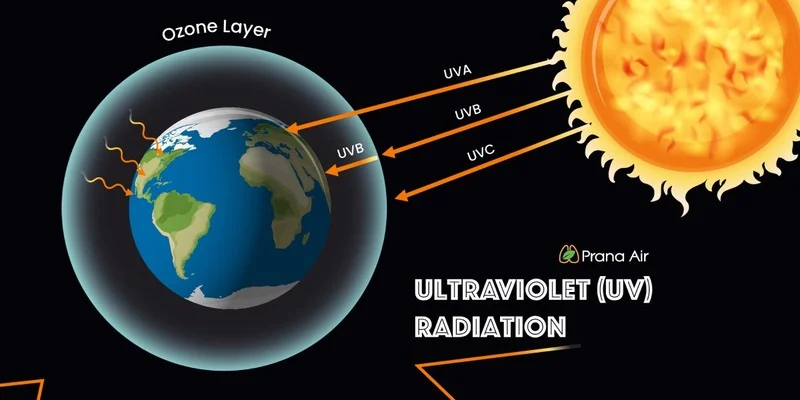
Ultraviolet radiation falls between visible light and X-rays on the electromagnetic spectrum, with wavelengths ranging from 10 nm to 400 nm. It is divided into three main types based on wavelength: UVA, UVB, and UVC. Each type has different effects on living organisms and materials.
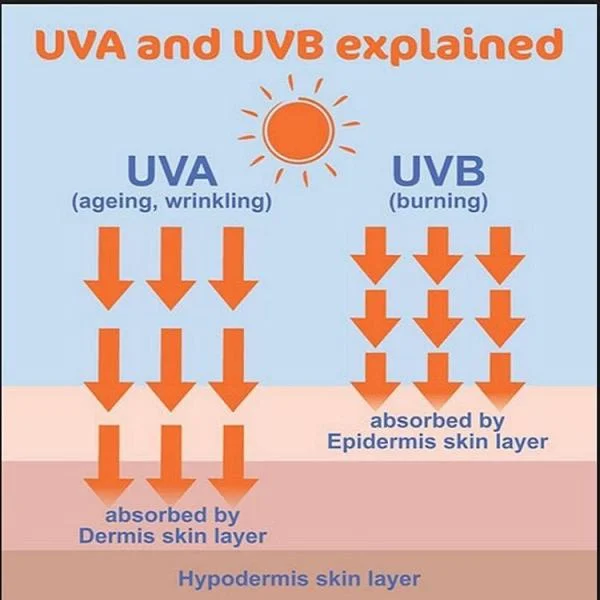
- UVA (315-400 nm): This is the least harmful form of UV radiation but can penetrate deep into the skin, contributing to premature aging and skin cancer.
- UVB (280-315 nm): UVB rays are more harmful than UVA as they affect the outer layers of the skin, causing sunburn and playing a significant role in the development of skin cancer.
- UVC (100-280 nm): UVC is the most dangerous type, but fortunately, it is mostly absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer and does not reach the ground.
Benefits of Ultraviolet Radiation
Despite its risks, ultraviolet radiation has several important benefits and practical applications.
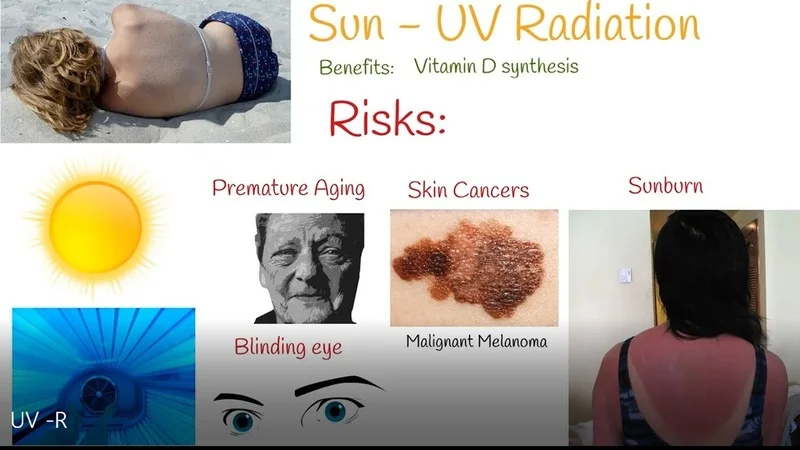
- Vitamin D Synthesis: One of the most well-known benefits of UVB radiation is its role in synthesizing vitamin D in the skin. Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining healthy bones and a strong immune system.
- Sterilization and Disinfection: UV radiation, particularly UVC, is widely used for sterilizing medical equipment, water, and air. Its ability to destroy bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens makes it invaluable in hospitals and laboratories.
- Phototherapy: UV light is used in the treatment of various skin conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema. Controlled exposure to UVB light can reduce symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients.
- Tanning: UV radiation, specifically UVA and UVB, is responsible for tanning the skin. While tanning can be a cosmetic benefit, it should be done cautiously to avoid overexposure.
Risks of Ultraviolet Radiation
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation poses several health risks, which are important to understand for proper protection.
- Skin Cancer: The most significant risk of UV radiation is skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form. Prolonged exposure to UVB radiation is a major risk factor for developing skin cancer.
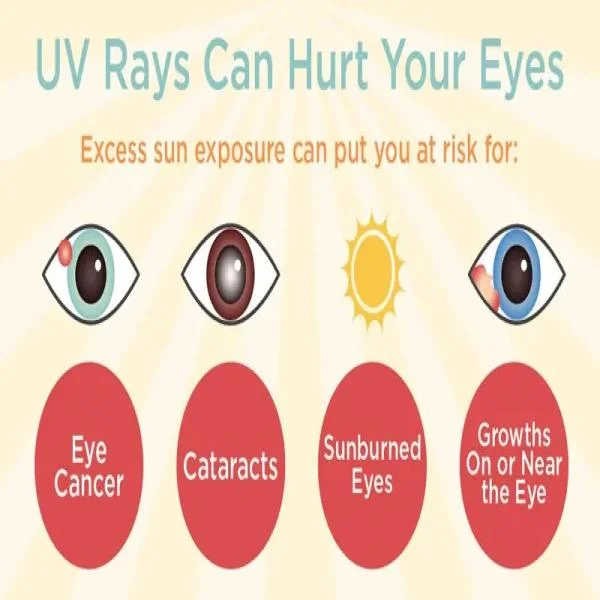
- Eye Damage: UV radiation can cause severe eye damage, including cataracts, macular degeneration, and photokeratitis, a painful condition also known as "snow blindness."
- Premature Aging: Overexposure to UVA rays can accelerate the aging process of the skin, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of elasticity.
- Immune System Suppression: Excessive UV exposure can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and reducing the effectiveness of vaccines.
Applications of Ultraviolet Radiation
UV radiation has a wide range of applications across various industries, from healthcare to environmental science.
- Water and Air Purification: UVC radiation is widely used in water treatment facilities to disinfect drinking water and wastewater. It is also employed in air purification systems to eliminate airborne pathogens in hospitals, offices, and homes.
- Medical Applications: Beyond sterilization, UV radiation is used in phototherapy for treating skin conditions and certain types of jaundice in newborns. It is also being explored for its potential in treating some cancers.
- Forensic Science: UV light is used in forensic science to detect bodily fluids, fingerprints, and other evidence that may be invisible to the naked eye. It helps in crime scene investigations and the identification of counterfeit currency and documents.
- Agriculture: UV radiation is utilized in agriculture to control pests and diseases. UV light traps can attract and kill insects, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
- Cosmetics and Dermatology: UV light is used in the beauty industry for tanning beds and nail curing lamps. However, these applications should be approached with caution due to the associated health risks.
Protection Against Ultraviolet Radiation

Given the risks associated with UV radiation, it’s crucial to take protective measures, especially when spending time outdoors.
- Sunscreen: Using broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays is essential. Reapplying sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating, offers better protection.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts, and UV-blocking sunglasses, can significantly reduce UV exposure.
- Avoiding Peak Sun Hours: The intensity of UV radiation is highest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Limiting sun exposure during these hours can lower the risk of skin damage.
- Shade: Seeking shade whenever possible, especially during peak sun hours, provides an additional layer of protection against UV rays.
Conclusion
Dong A has shared with readers the essential knowledge about the nature of ultraviolet radiation, its benefits and applications in different fields. While ultraviolet radiation is indispensable for certain medical and industrial applications, excessive exposure can have serious health consequences.
If you need more references about our water treatment products, please visit the official website of Dong A Chemical at dongachem.com or call a hotline (+84) 985797941 to receive advice and support from the experienced consultant.
Related Articles
Why Pool Electrolysis Is Key to Cleaner, Healthier Swimming Pools
Pool maintenance is essential to owning a swimming pool, ensuring the water remains clean, safe, and ...
Applications Electrolysis of Salt Water and How It Works?
Electrolysis of salt water is a fascinating chemical process with broad applications, from producing ...
Benefits of Using an Ozone Generator for Water Treatment
In recent years, the use of ozone generators for water treatment has gained widespread popularity. ...
What You Need to Know UVA and UVB Rays for Skin Protection
Sunlight plays an essential role in human health, providing Vitamin D and improving mood. However, ...
How Can UV Rays Damage Eyes and How to Protect Them
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can cause significant damage to your eyes over ...
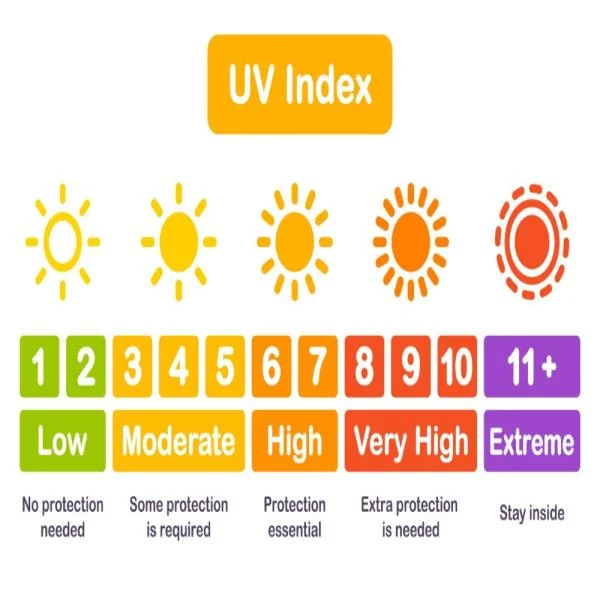
What Is the UV Index and Why It Matters for Your Skin and Health
The UV Index is a critical tool for understanding the levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the ...