Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can cause significant damage to your eyes over time. While most people are aware of the harmful effects of UV rays on their skin, fewer understand the risks they pose to eye health. UV radiation, particularly UVA and UVB rays, can contribute to various eye conditions, some of which may lead to vision loss if left untreated. This article explores to UV rays damage eyes , providing insights into how you can protect your eyes from these harmful effects.
What Are UV Rays?
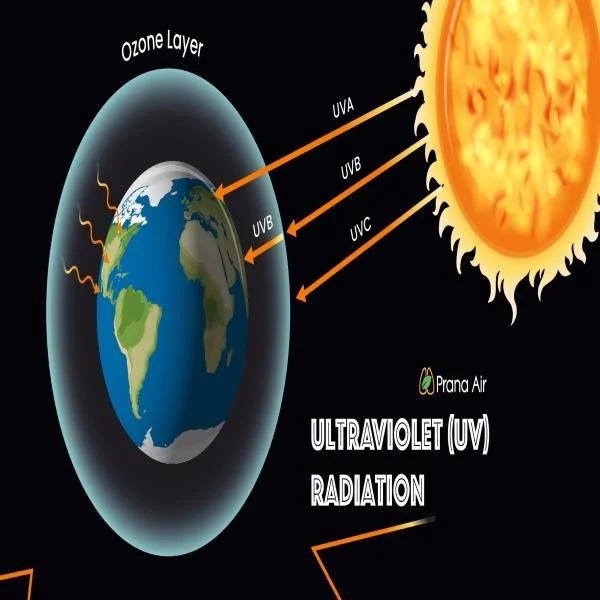
UV rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. They are invisible to the human eye and come in three main types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. While UVC rays are mostly blocked by the Earth’s atmosphere, UVA and UVB rays can penetrate the atmosphere and reach the surface. These rays are responsible for both short-term and long-term damage to your eyes.
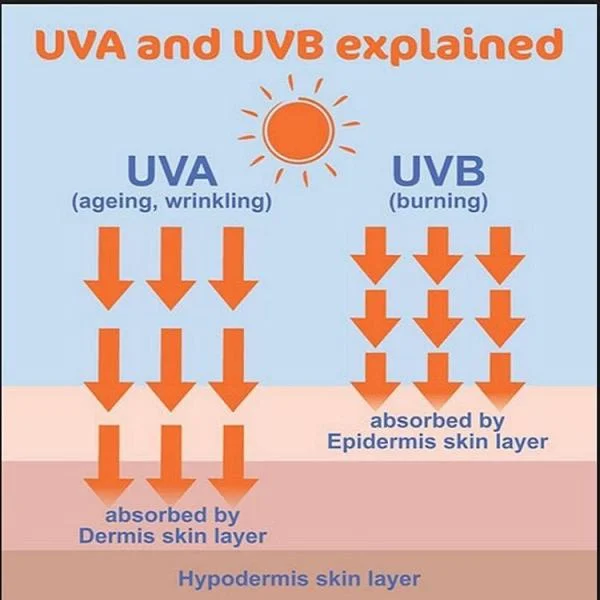
- UVA Rays : These rays have longer wavelengths and can penetrate deeper into the skin and eyes. While less intense than UVB rays, UVA rays are more abundant and can cause cumulative damage over time, leading to conditions like cataracts and macular degeneration.
- UVB Rays : UVB rays have shorter wavelengths but are more intense than UVA rays. They are primarily responsible for sunburns and are also a significant contributor to eye problems such as photokeratitis (sunburn of the eye) and cataracts.
How UV Rays Damage the Eyes
The eyes are particularly vulnerable to UV radiation because they are exposed to sunlight every day, even on cloudy days or in the winter. Overexposure to UV rays can lead to several serious eye conditions:
- Cataracts : A cataract is a clouding of the eye’s lens, which can result in blurred vision and eventual blindness if untreated. Research has shown that prolonged exposure to UVB rays increases the risk of developing cataracts. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that up to 20% of cataract cases may be caused by UV radiation.
- Macular Degeneration : The macula is a small part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. Long-term exposure to UVA rays can lead to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a condition that affects the macula and results in vision loss in the central field of vision.
- Photokeratitis : Sometimes referred to as “sunburn of the eye,” photokeratitis occurs when the cornea is damaged by UVB rays. This condition can cause pain, redness, blurred vision, and in severe cases, temporary blindness. It is often experienced by people who spend extended periods outdoors without eye protection, especially in snowy or reflective environments where UV rays are more intense.
- Pterygium : This condition is characterized by a growth of tissue on the white part of the eye that can eventually spread to the cornea, affecting vision. Pterygium is more common in people who are regularly exposed to UV rays, particularly in regions with high levels of sunlight.
- Pinguecula : Pinguecula is a yellowish growth on the white part of the eye, often resulting from chronic exposure to UV rays. While it may not interfere with vision initially, it can become irritated or lead to discomfort, especially in dry or dusty environments.
Risk Factors for UV-Related Eye Damage
Several factors can increase your risk of eye damage from UV rays, including:
- Geographical Location : People living closer to the equator are exposed to higher levels of UV radiation due to the sun's direct overhead position.
- Time of Day : UV radiation is strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so spending time outdoors during these hours increases your risk of exposure.
- Season : While UV rays are present year-round, they are more intense during the summer months, especially in tropical and subtropical regions.
- Altitude : The higher the altitude, the greater the UV exposure. This is why people who spend time in mountainous regions, such as hikers or skiers, are at a higher risk of UV-related eye conditions.
- Reflection : Surfaces like water, snow, sand, and pavement can reflect UV rays, effectively doubling your exposure. For example, snow reflects up to 80% of UV rays, making it crucial to wear eye protection during winter sports or activities.
How to Protect Your Eyes from UV Rays
The good news is that there are several ways to protect your eyes from the harmful effects of UV radiation. Here are some key strategies to reduce your exposure and safeguard your vision:
- Wear UV-Blocking Sunglasses : Not all sunglasses offer adequate UV protection. Look for sunglasses that block 100% of both UVA and UVB rays. Wraparound sunglasses are especially effective because they protect the eyes from UV rays entering from the sides.
- Use a Wide-Brimmed Hat : Wearing a hat with a brim that extends at least three inches can reduce UV exposure to your eyes by up to 50%. This is particularly useful when combined with UV-blocking sunglasses for full protection.
- Consider Contact Lenses with UV Protection : Some contact lenses are designed to block a significant amount of UV rays. While they don’t offer complete protection, they can provide an added layer of defense when used with sunglasses.
- Avoid Direct Sun Exposure : If possible, limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during peak UV hours. Seek shade outdoors and avoid activities that expose your eyes to intense sunlight without protection.
- Use UV-Protective Eyewear During Outdoor Activities : If you’re engaging in outdoor sports or activities, especially those involving reflective surfaces like skiing, boating, or hiking, wear eyewear designed to protect against UV rays.
- Be Aware of Reflected UV Rays : As mentioned, reflective surfaces like water, snow, and sand can increase UV exposure. Take extra precautions in these environments by wearing protective gear.
Regular Eye Check-Ups
Regular eye exams are essential for monitoring eye health and early detection of UV-related damage. Eye care professionals can detect conditions like cataracts, macular degeneration, or pterygium in their early stages, allowing for prompt treatment and management.
Conclusion
Dong A has shared with readers essential knowledge about how UV rays damage eyes , providing insights into how you can protect your eyes from these harmful effects . UV rays pose a significant threat to your eyes, with potential long-term consequences such as cataracts, macular degeneration, and other serious conditions.
If you need more references about our water treatment products, please visit the official website of Dong A Chemical at dongachem.com or call a hotline (+84) 985797941 to receive advice and support from the experienced consultant.
Related Articles
What You Need to Know UVA and UVB Rays for Skin Protection
Sunlight plays an essential role in human health, providing Vitamin D and improving mood. However, ...
Understanding Ultraviolet Radiation: Benefits, Risks, and Applications
Ultraviolet radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that comes primarily from the sun. ...
Why Pool Electrolysis Is Key to Cleaner, Healthier Swimming Pools
Pool maintenance is essential to owning a swimming pool, ensuring the water remains clean, safe, and ...
What Is the UV Index and Why It Matters for Your Skin and Health
The UV Index is a critical tool for understanding the levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the ...
Why UV Water Treatment is the Solution to Clean Water
Ultraviolet water treatment is becoming an increasingly popular method for purifying water in homes, ...
What You Need to Know Alum Treatment for Pools
Alum treatment , also known as aluminum sulfate treatment, is a widely used method for improving ...