The UV Index is a critical tool for understanding the levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and how it can affect your health. Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), the UV Index helps people gauge the daily risk of UV exposure, which is essential for protecting the skin and eyes from harmful effects like sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer. In this article, we'll explore what the UV Index is, how it’s measured, and why it’s important for your overall health and well-being.
What Is the UV Index?
The UV Index is a standardized scale designed to measure the strength of ultraviolet radiation at a specific time and location. It ranges from 0 to 11+, with higher numbers indicating greater UV exposure risk. This scale is used globally, providing a clear and accessible way to communicate the potential harm caused by the sun’s rays. The UV Index typically reflects the level of UV radiation for midday when the sun is at its highest point, but the level of risk can vary throughout the day.
- 0-2 (Low Risk): Minimal risk of harm from UV exposure for most individuals. People can safely spend time outdoors without the need for much sun protection.
- 3-5 (Moderate Risk): Some risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Individuals should consider sun protection measures, especially during midday.
- 6-7 (High Risk): High risk of harm from UV radiation. Sun protection, such as wearing sunglasses, applying sunscreen, and seeking shade, is highly recommended.
- 8-10 (Very High Risk): Very high risk of harm. Full sun protection is necessary to prevent skin damage and other health issues.
- 11+ (Extreme Risk): Extreme risk of harm from UV radiation. Unprotected skin and eyes can burn in minutes, and sun exposure should be avoided as much as possible.
How the UV Index Is Measured
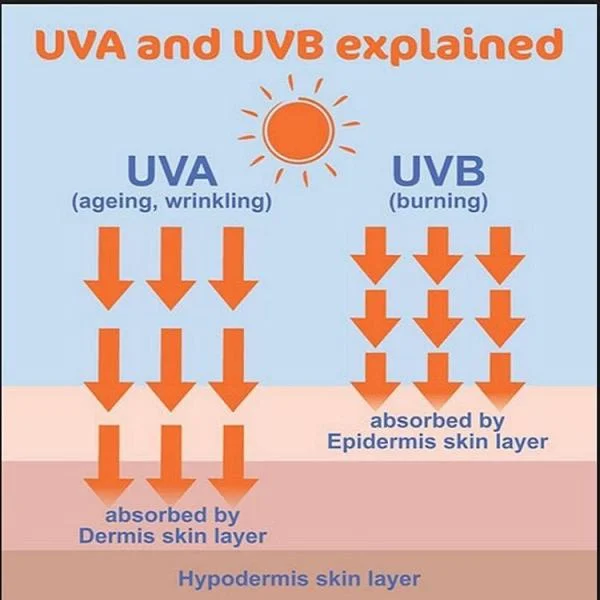
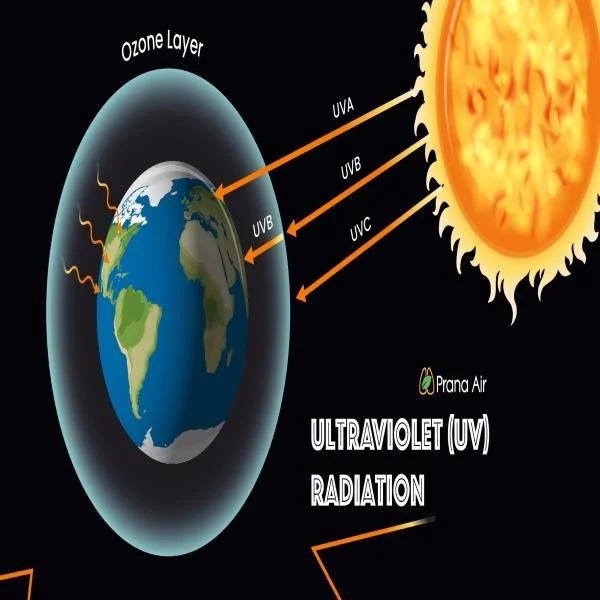
The UV Index is calculated based on several factors, including the time of day, geographic location, altitude, and cloud cover. It considers both UVA and UVB rays, the two types of ultraviolet radiation that affect the Earth’s surface.
- UVA Rays : These rays penetrate deeper into the skin and are responsible for long-term effects like wrinkles and premature aging. While less intense than UVB rays, they can cause cumulative damage over time.
- UVB Rays : These rays are more intense and are the main cause of sunburn. They are also closely linked to the development of skin cancer.
Meteorological organizations and health agencies calculate the UV Index by taking satellite data and ground measurements of UV radiation. This information is then used to predict the daily UV Index for specific locations, allowing people to make informed decisions about sun exposure.
Why the UV Index Matters
The UV Index is essential for maintaining good skin health and preventing serious conditions such as skin cancer. Overexposure to UV radiation can have a wide range of negative effects on your body, many of which are preventable if you understand and use the UV Index properly.
1. Skin Cancer Risk
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation is the leading cause of skin cancer, including both non-melanoma and melanoma types. Even on days when the UV Index is moderate or high, spending long periods in the sun without protection can significantly increase your risk of developing skin cancer.
- Melanoma: This is the most dangerous form of skin cancer and is directly linked to high exposure to UVB radiation. It can spread to other parts of the body and, if not detected early, may be life-threatening.
- Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas: These are more common but less dangerous than melanoma. They primarily affect areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and hands.
2. Premature Aging
High levels of UVA exposure are associated with premature aging of the skin. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin layers, damaging collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles, sagging skin, and age spots. By checking the UV Index and taking protective measures, you can help reduce the risk of these cosmetic issues.
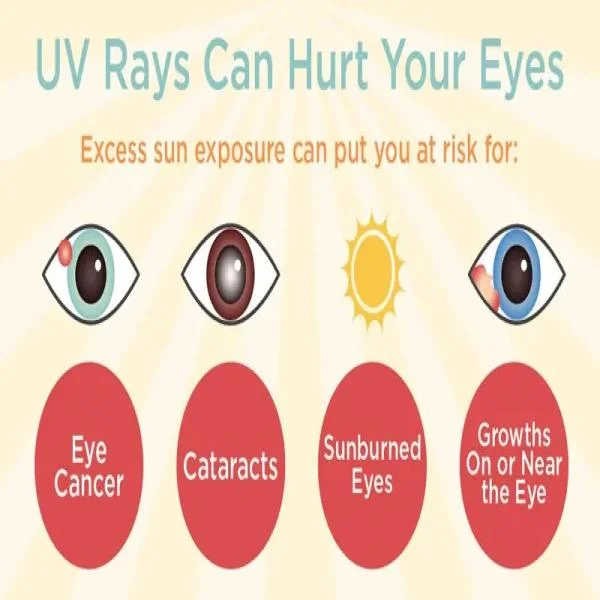
3. Eye Damage
UV radiation doesn't just affect your skin. It can also damage your eyes, leading to conditions such as cataracts and macular degeneration, both of which can result in impaired vision or blindness. UV exposure can also cause photokeratitis, a painful condition similar to a sunburn on the cornea.
4. Immune System Suppression
Overexposure to UV radiation can suppress the immune system, reducing its ability to fight off infections and increasing the risk of illness. This is particularly concerning for people who are already immunocompromised.
How to Use the UV Index to Protect Yourself
Using the UV Index as part of your daily routine can help you make informed decisions about how to protect yourself from harmful UV radiation. Here are some practical ways to use the UV Index to reduce your risk of sun damage:
1. Sunscreen Use
When the UV Index is 3 or higher, it’s important to apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to all exposed skin. Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, or more often if you are swimming or sweating.
2. Protective Clothing
Wearing UV-protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays, is essential when the UV Index is high. Darker colors and tightly woven fabrics offer the best protection.
3. Seek Shade
If the UV Index is in the high or very high range, try to stay in the shade between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV radiation is strongest. If you must be outdoors, ensure you take adequate sun protection measures.
4. Monitor UV Levels on Cloudy Days
Many people mistakenly believe that cloudy or overcast days protect from UV radiation. However, up to 80% of UV rays can still penetrate clouds, so it’s important to check the UV Index and take precautions even when the sun isn’t shining brightly.
5. Be Mindful of Reflective Surfaces
UV radiation can be reflected off surfaces like water, sand, and snow, increasing your exposure. If you’re at the beach, by the pool, or participating in winter sports, check the UV Index and take extra precautions.
Who Is Most at Risk?
While everyone is at risk for UV-related damage, certain groups are more susceptible to the harmful effects of UV radiation. These include:
- People with fair skin, light-colored eyes, and blonde or red hair : These individuals produce less melanin, the pigment that helps protect the skin from UV damage.
- Individuals with a family history of skin cancer : If skin cancer runs in your family, you are at a higher risk of developing the condition.
- Outdoor workers and athletes : People who spend long periods outdoors are exposed to more UV radiation and should take extra precautions.
- Children and adolescents : Young people are more vulnerable to UV damage, and protecting their skin early can prevent long-term health problems.
Conclusion
Dong A has shared with readers essential knowledge about what the UV Index is, and how it’s measured. The UV Index is a valuable tool for managing your exposure to ultraviolet radiation and protecting your skin and eyes from damage. By understanding how the UV Index works and following appropriate safety measures, you can enjoy the outdoors without putting your health at risk.
If you need more references about our water treatment products, please visit the official website of Dong A Chemical at dongachem.com or call a hotline (+84) 985797941 to receive advice and support from the experienced consultant.
Related Articles
How Can UV Rays Damage Eyes and How to Protect Them
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can cause significant damage to your eyes over ...
What You Need to Know UVA and UVB Rays for Skin Protection
Sunlight plays an essential role in human health, providing Vitamin D and improving mood. However, ...
Understanding Ultraviolet Radiation: Benefits, Risks, and Applications
Ultraviolet radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that comes primarily from the sun. ...
Why UV Water Treatment is the Solution to Clean Water
Ultraviolet water treatment is becoming an increasingly popular method for purifying water in homes, ...
What You Need to Know Alum Treatment for Pools
Alum treatment , also known as aluminum sulfate treatment, is a widely used method for improving ...
Alum Water: A Simple Solution for Clean Water and More
Alum water , a solution created by dissolving alum in water, has been used for centuries as a ...