Electrolysis of salt water is a fascinating chemical process with broad applications, from producing chlorine and hydrogen to water desalination. By passing an electric current through a saltwater solution, the water is split into its chemical components, creating valuable byproducts used in various industries. This eco-friendly process is increasingly essential for water purification, renewable energy, and chemical production. In this article, we'll explore how the electrolysis of salt water works, its significance, and its practical applications across industries.
What is the Electrolysis of Salt Water?
Electrolysis of salt water is a method that involves using electricity to decompose a solution of water (H 2 O) and salt, typically sodium chloride (NaCl), into its chemical components. The process results in the production of chlorine gas (Cl 2 ), hydrogen gas (H 2 ), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Here's how it works:
- Two electrodes (an anode and a cathode) are placed into a saltwater solution.
- A direct current (DC) is applied, causing the electrical energy to break the bonds in the salt and water molecules.
- At the anode, chlorine gas is produced, while hydrogen gas is generated at the cathode. Remaining in the solution is sodium hydroxide.

The overall chemical reaction for the electrolysis of salt water can be summarized as follows:
2NaCl(aq) + 2H 2 O (l) → Cl 2 (g) + H 2 (g) + 2NaOH (aq)
This process is a simple yet highly efficient way of producing essential chemicals used across a range of industries.
Chemistry of Salt Water Electrolysis
The process of electrolysis is a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction, where different reactions occur at each electrode. Below are the key reactions involved in the electrolysis of salt water:
- At the Anode (Oxidation) : Chloride ions (Cl-) are oxidized to produce chlorine gas
2H 2 O (l) → O 2 (g) + 4H+ (aq.) + 4e–
- At the Cathode (Reduction) : Water is reduced to hydrogen gas (H2) and hydroxide ions (OH-):
2H+ (aq.) + 2e– → H 2 (g)
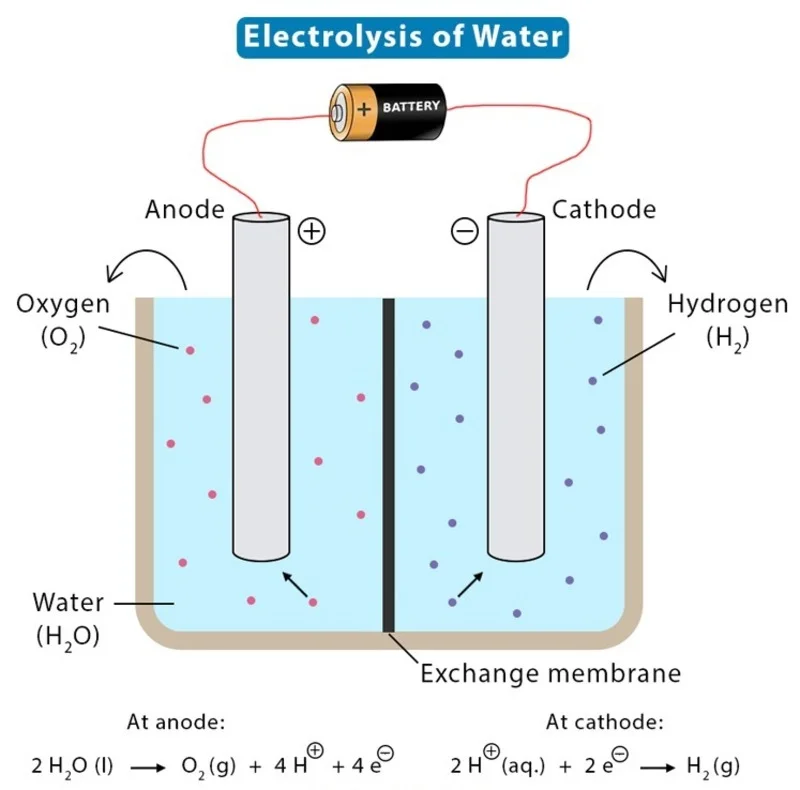
These reactions result in the formation of chlorine gas at the anode, hydrogen gas at the cathode, and sodium hydroxide in the remaining solution.
Applications of Salt Water Electrolysis
The electrolysis of salt water is a versatile process with applications across several industries, making it an indispensable tool in chemical manufacturing, energy production, and water purification.
Chlorine Production
One of the primary applications of saltwater electrolysis is the production of chlorine gas. Chlorine is often used in:
- Disinfection : Chlorine is a powerful disinfectant, commonly used in water treatment facilities to purify drinking water and swimming pools.
- Manufacturing : It's a key component in producing polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for plastic production, as well as household cleaning products.
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen gas, a byproduct of the electrolysis of salt water, is emerging as a clean and renewable energy source. Known as "green hydrogen" when produced using renewable energy, it has the potential to replace fossil fuels in:
- Transportation : Hydrogen fuel cells power electric vehicles, producing only water as a byproduct.
- Energy Storage : Hydrogen can store excess renewable energy generated by solar and wind farms.
Sodium Hydroxide (Caustic Soda) Production
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), also known as caustic soda, is another valuable byproduct of the electrolysis of salt water. It is used in:
- Soap and Detergent Manufacturing : Sodium hydroxide is a key ingredient in producing soaps and detergents.
- Paper Production : It is also used in the pulp and paper industry to process wood into paper.
- Textile Industry : Sodium hydroxide plays a role in the processing and dyeing of fabrics.
Purification of Water and Desalination
The electrolysis of salt water is increasingly applied in water purification and desalination efforts, particularly in regions where freshwater is scarce. Through electrolysis, salt is broken down, and the water is purified, making it safe for drinking and irrigation. This method is especially useful in areas with high salinity or limited access to freshwater resources.
Environmental Cleanup
Saltwater electrolysis is also used to treat industrial wastewater by breaking down harmful pollutants and reducing environmental contamination. This process has significant potential for use in industries like mining, textiles, and chemical production, where wastewater often contains hazardous materials.
Advantages of Electrolysis of Salt Water
There are several benefits to using electrolysis for chemical production and water treatment:
- Eco-Friendly : When powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind, electrolysis produces no harmful emissions, making it an environmentally friendly solution for producing chemicals and treating water.
- Resource Abundance : Saltwater is readily available, especially in coastal areas, making it an accessible and sustainable resource for industries.
- Multiple Byproducts : Electrolysis generates useful byproducts such as chlorine, hydrogen, and sodium hydroxide, which can be repurposed for various applications, improving efficiency.
- Water Treatment : Electrolysis helps disinfect and purify water, making it a valuable tool for improving water quality in residential, industrial, and municipal settings.
Challenges of Salt Water Electrolysis
Despite its many benefits, the electrolysis of salt water faces several challenges:
- Energy Consumption : The process requires a significant amount of electricity, making it energy-intensive. Using renewable energy can mitigate environmental impact, but it's not always available.
- Corrosion : Chlorine gas produced during electrolysis can cause corrosion of the equipment, leading to maintenance challenges and increased operational costs.
- Setup Costs : The equipment required for large-scale electrolysis can be expensive, creating high initial setup costs, although long-term benefits often justify the investment.
- Handling Byproducts : Chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide require careful handling and storage due to their hazardous nature. To avoid accidents, certain safety procedures are necessary.
Future of Salt Water Electrolysis
The future of saltwater electrolysis is promising, particularly with growing interest in sustainable energy. As demand for hydrogen fuel increases, electrolysis could become a key player in a future hydrogen-based economy. Advances in technology, such as more efficient electrodes and renewable energy sources, are likely to make the process more cost-effective and environmentally sustainable.
Ongoing research into making the electrolysis process more energy-efficient is also expected to reduce costs and expand its applications in water treatment and industrial processes.
Conclusion
Dong A has given readers the most essential information regarding the workings electrolysis of salt water. Electrolysis of salt water is a powerful and versatile chemical process with applications ranging from chlorine production and water treatment to green hydrogen generation.By harnessing this eco-friendly process, we can create a more sustainable and cleaner future for chemical production and energy use.
If you need more references about our water treatment products, please visit the official website of Dong A Chemical at dongachem.com or call a hotline (+84) 985797941 to receive advice and support from the experienced consultant.
Related Articles
Benefits of Using an Ozone Generator for Water Treatment
In recent years, the use of ozone generators for water treatment has gained widespread popularity. ...
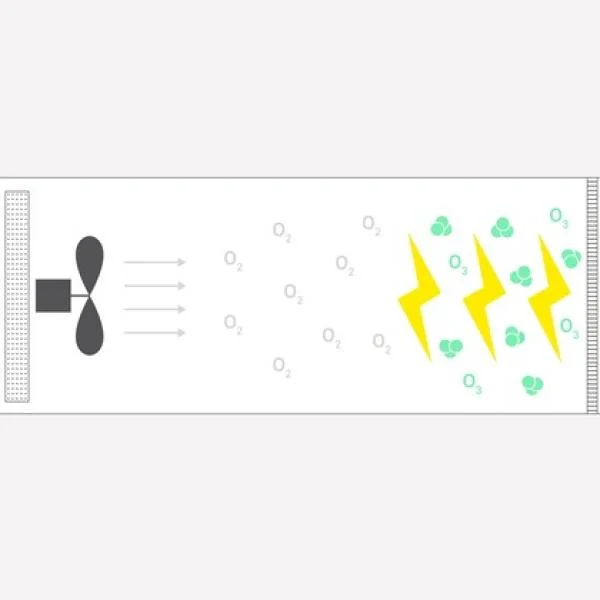
Water Purification by Ozone and How Does It Work?
Ozone (O₃) is a powerful natural molecule known for its critical role in water purification. It is a ...
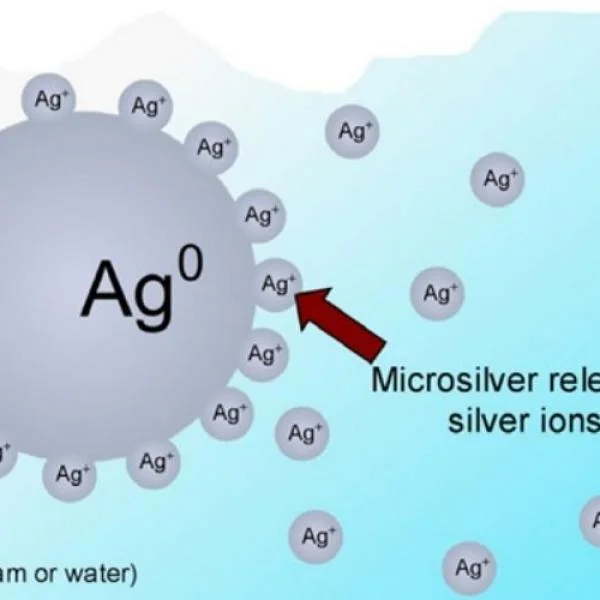
The Science Behind Silver Ions: A Powerful Antimicrobial Agent
Silver ions have emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against harmful microorganisms. This ...
Why Pool Electrolysis Is Key to Cleaner, Healthier Swimming Pools
Pool maintenance is essential to owning a swimming pool, ensuring the water remains clean, safe, and ...
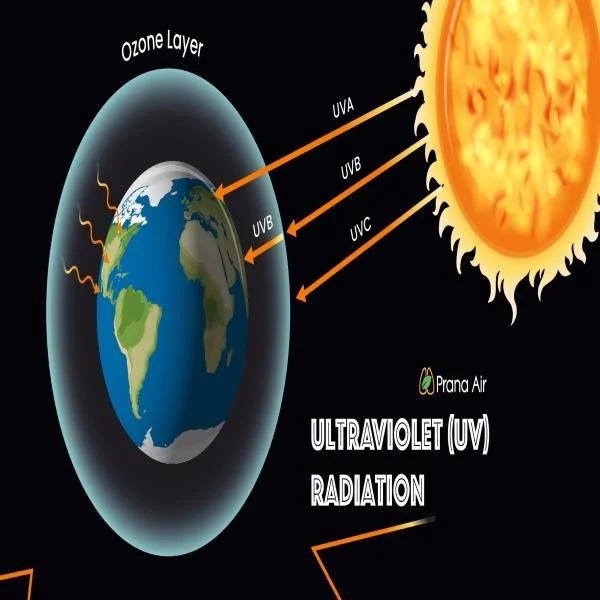
Understanding Ultraviolet Radiation: Benefits, Risks, and Applications
Ultraviolet radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that comes primarily from the sun. ...
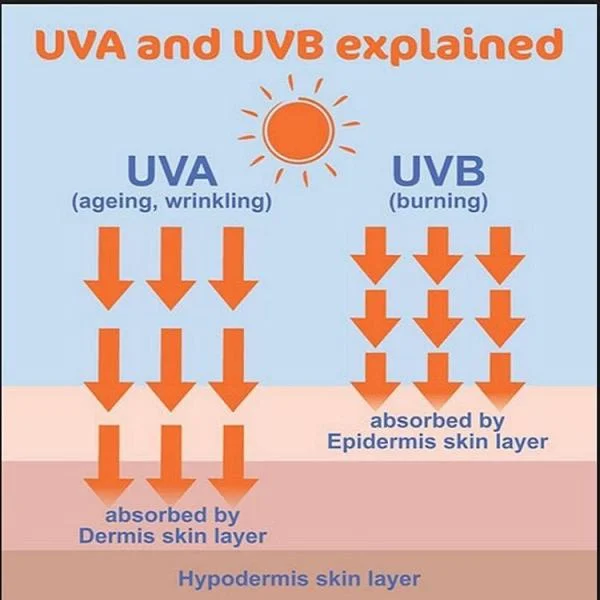
What You Need to Know UVA and UVB Rays for Skin Protection
Sunlight plays an essential role in human health, providing Vitamin D and improving mood. However, ...