Calcium hypochlorite is commonly used as a disinfectant. This disinfectant chemical widely used for a long time to control and prevent the spread of infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungal and other microorganisms. Dong A Chemical invites readers to learn more about this topic in detail in this article.
Overview of Calcium Hypochlorite Chemical
Calcium hypochlorite, with the molecular formula Ca(ClO)2, is a widely used chemical compound known for its powerful oxidizing properties and its extensive applications in various industries. It is available in various forms, including granules, tablets, or powder, and has a white or off-white color. Besides, it has a strong chlorine smell and can dissolve in water. Calcium hypochlorite is widely used for water treatment as well as disinfecting surfaces, tools, and facilities.
Ca(ClO)2 is relatively stable in dry conditions but decomposes in the presence of moisture, heat, or acids.

Composition of Calcium Hypochlorite Chemical
Calcium hypochlorite is formed from the salt of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl). It has the chemical formula Ca(ClO)2 with a molecular weight of 142.98 g/mol. Chemical Ca(ClO)2 has a weight percentage of 65% to 70% accessible chlorine, which indicates how effective it is in cleaning. The substance can break quickly in the presence of acids, heat, or sunshine, producing chlorine gas while remaining stable under normal circumstances.
When chemical Ca(ClO)2 is dissolved in water, hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is released, which is primarily what causes the disinfection action. Strong oxidants, such as hypochlorous acid, may break down cell membranes and cause damage to DNA, proteins, and enzymes. Additionally, the Ca(ClO)2 solution’s high pH may enhance its disinfectant properties by compromising the integrity of cell membranes.
Chemical Properties and Effects of Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hypochlorite has several effects due to its strong oxidizing and disinfecting properties when it comes into contact with other substances or materials. Here are some of the key effects of Ca(ClO)2
Effective against bacteria
Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria are both highly vulnerable to calcium hypochlorite’s powerful antibacterial effects. Many factors, including the quantity and duration of the solution's contact time, the pH of the water, and the type of bacteria being treated, can affect calcium hypochlorite’s ability to kill bacteria.
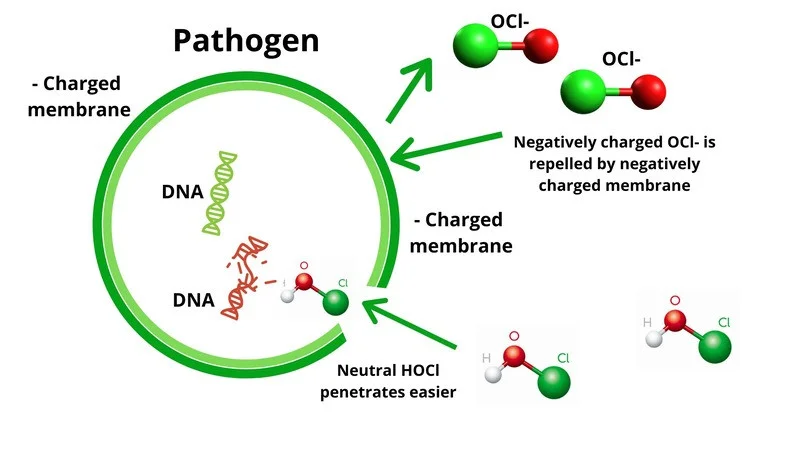
According to studies, Ca(ClO)2 may decrease bacteria by 99% when applied at 200–500 ppm concentrations and 1–10 min exposure intervals. However, if using Ca(ClO)2 solutions up to 1000 ppm in concentration, bacterial populations can be reduced by 99% in approximately 30 seconds. Calcium hypochlorite’s disinfectant action is significantly influenced by the pH of the water, with the best results being at a pH of 6.5 to 7.5.
Effective against viruses
Ca(ClO)2 is also very powerful against viruses, both enclosed and non-enveloped. The lipid envelope that surrounds enveloping viruses, including coronaviruses and influenza viruses, makes them susceptible to disinfectants like Ca(ClO)2 chemical.
According to studies, Ca(ClO)2, when employed at concentrations between 500 and 1000 ppm and exposure intervals of 5 to 10 minutes, may eliminate viral by 99.9%. Higher concentrations of up to 5000 ppm can eliminate 99% of the viral population in as little as 30 seconds. The kind of virus, solution concentration, contact time, and presence of organic matter are all factors that impact calcium hypochlorite’s ability to disinfect against viruses.
Effective anti-fungal
Ca(ClO)2 is effective against several fungal species, including molds and yeasts. However, fungal spores have a strong shell that protects them from disinfectants. Aspergillus, Candida, and Penicillium are just a few of the fungal that it is successful against.
When employed at concentrations between 200 and 1000 ppm and exposure durations between 10 and 60 minutes, studies have shown that Ca(ClO)2 may eliminate the fungus population by 99.9%. Higher concentrations of up to 5000 ppm can eliminate the fungus population by 99.999% in just 5 minutes. The kind of fungus, solution concentration and contact duration, as well as the presence of organic materials, all affect calcium hypochlorite’s capacity to disinfect fungal.
Effective against protozoa
Calcium hypochlorite can eliminate protozoa, especially aquatic parasites such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium. Although this chemical can effectively remove these parasites from water and are resistant to many disinfectants, they can cause gastrointestinal sickness.
When used at concentrations between 10 and 15 ppm and with exposure lengths of at least an hour, Ca(ClO)2 may reduce the protozoa of Cryptosporidium and Giardia by 99%. Protozoa populations can be reduced by 99% in approximately 10 minutes with higher concentrations of up to 50 ppm. The type of parasite, the solution's concentration and contact time, the presence of organic matter, and other factors affect the calcium hypochlorite’s ability to disinfect protozoa.
The effects of Ca(ClO)2 are primarily due to its strong oxidizing and disinfecting properties, which make it useful for various applications. It also requires proper handling and precautions to minimize potential hazards and environmental impacts.
Summary
The above article introduces the disinfection mechanism of calcium hypochlorite. Hopefully, the knowledge we share will help readers in applying it in practice. To find out more useful information, please learn more by reading the articles on Dong A Chemical’s website.
Related Articles
What is chlorine dioxide? Address supplier chlorine dioxide quality assurance
Chlorine dioxide is famous for its antibacterial and water treatment and is an extremely powerful ...
Compared Calcium Hypochlorite to Other Chlorine-based Disinfectants
Calcium hypochlorite is one of the most commonly used chlorine-based disinfectants. Chlorine-based ...
Dong A Chemical – Global Chlorine Supplier
Dong A Chemical - Manufacturer and Global Supplier of Chlorine. Owning a large-scale production ...
What is a Chlorine Oxide Compound? Properties and Applications of Compound in Life
Chlorine oxide is a gas used in extremely small amounts to disinfect water. It is a disinfectant ...
What is Chlorine? Properties and Applications of Chlorine Compound in Life
Chlorine is one of the simplest and most common compounds in chemistry. It was discovered in the ...
The Benefits and Best Application of Using Liquid Chlorine for Pool Maintenance
Using liquid chlorine for pools is one of the most effective methods for ensuring the water remains ...