When it comes to maintaining a swimming pool, keeping your water balanced is essential. One key factor often overlooked is hardness in pool water, specifically calcium hardness. This crucial element can significantly impact the overall health of your pool, the longevity of its components, and the comfort of your swimming experience. In this article, we’ll explore what calcium hardness is, its importance, how to maintain it, and how to address common problems associated with it.
Causes of Excess Pool Calcium
Excess calcium in pool water is often the result of an imbalance in water chemistry. High pH levels and improper alkalinity can increase the likelihood of calcium precipitation, leading to scaling and cloudy water. Without proper monitoring and maintenance, these chemical imbalances can quickly disrupt the stability of your pool.
Temperature fluctuations are another significant factor contributing to excess calcium. Calcium is more soluble in cold water, so as the water temperature rises, calcium tends to precipitate and form deposits on heaters and pipes. Evaporation further concentrates calcium in pool water, especially in areas with high temperatures, making consistent maintenance even more crucial.

Excess calcium in pool water is often the result of an imbalance in water chemistry
What is Calcium Hardness?
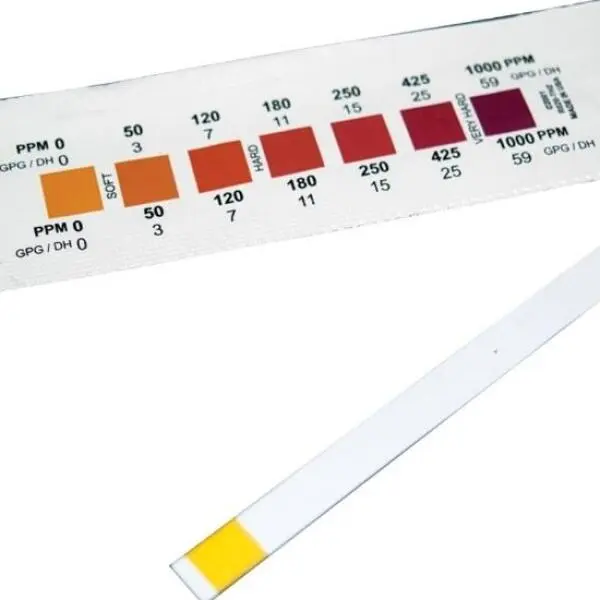
Calcium hardness refers to the measure of dissolved calcium and magnesium salts in your pool water, often expressed in parts per million (ppm). This measurement determines how "soft" or "hard" the water is. Proper calcium levels contribute to the structural integrity of your pool, helping to maintain surfaces like plaster, grout, and tiles. For pools, the ideal range of calcium hardness is between 200–400 ppm, while for spas, it should be between 150–250 ppm.
Calcium hardness plays a vital role in protecting your pool from damage and ensuring smooth operation. If the calcium level is not properly managed, your pool's surfaces and equipment can deteriorate over time. Ensuring the correct balance can save you from expensive repairs and keep your pool visually appealing.
What are The Effects of Calcium Imbalance?
If your pool water has insufficient calcium, you can raise the hardness level by adding calcium chloride. This compound comes in granular or flaky forms and is easy to apply. Start by dissolving it in a bucket of water before pouring the solution into the pool. This process avoids direct contact with the skin, as calcium chloride generates heat when it reacts with water. Another option is to spread the granules evenly across the pool surface using a scoop, stirring until they dissolve completely.
On the other hand, lowering calcium hardness is essential if the levels are too high. Using a sequestering agent is an effective solution, as it binds excess calcium and prevents issues like scaling and staining. This chemical should be a part of your regular pool maintenance if you live in an area prone to hard water. Diluting your pool water with fresh water is another practical method to reduce calcium levels when necessary.

What are the effects of calcium imbalance?
Impact of Calcium Imbalance
Low calcium hardness can lead to serious problems for your pool. When the water lacks sufficient calcium, it becomes aggressive, drawing the mineral from surfaces and components to reach equilibrium. This can cause plaster and grout to etch, concrete to leach minerals, and metal fittings to corrode. Over time, these issues may result in leaks, unsightly stains, and costly repairs.
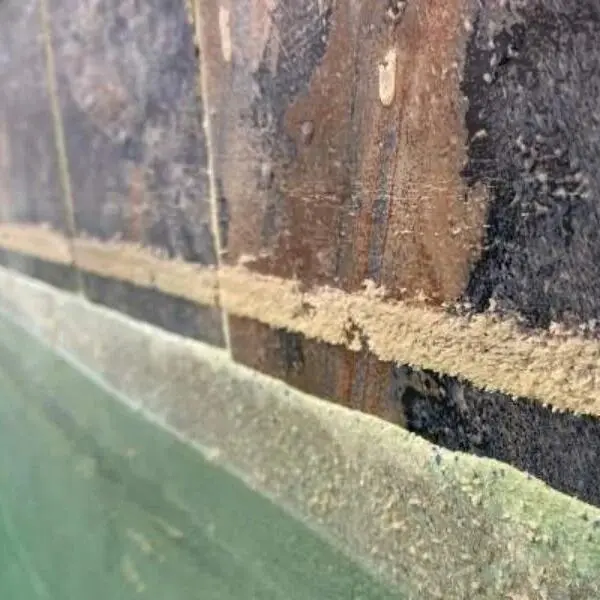
High calcium hardness also brings a host of challenges. It can cause cloudy water and leave rough, scaly deposits on pool surfaces. Additionally, it may clog plumbing systems and damage pool equipment, leading to inefficient operation. Metal fittings can also rust due to excessive calcium, further compromising the structural integrity and appearance of your pool. These problems emphasize the importance of maintaining balanced calcium levels.
Why Balance is Crucial
Maintaining the proper balance of calcium hardness in pool water is critical for both the structural health of your pool and the quality of the swimming experience. When calcium levels are too low, the water aggressively seeks to extract minerals from pool surfaces, causing damage to plaster and grout. On the other hand, excessive calcium results in scaling and cloudy water, creating an unpleasant environment for swimmers.
Striking the right balance helps protect pool components, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure safe and comfortable swimming conditions. The ideal calcium hardness range of 200–400 ppm prevents both scaling and corrosive water effects. Regular testing and adjustments can help maintain this balance, providing peace of mind for pool owners.
Regulating Calcium Hardness
Regular water testing is key to maintaining the correct calcium hardness levels. Using pool test strips or kits, you can measure calcium alongside other parameters like pH, alkalinity, and chlorine. For those new to pool maintenance, starting with easy-to-use test strips is a good option. You can also consult professionals for more accurate testing and advice.
Consistent chemical maintenance is essential for managing calcium hardness. This includes using a hardness increaser when levels are too low and a sequestering agent when they are too high. Additionally, monitoring pH and alkalinity levels helps maintain overall water balance. In areas with hard water, adopting a routine that includes diluting pool water or adding sequestering agents can significantly reduce calcium-related problems.

Regulating Calcium Hardness
Dealing with Calcium Buildup
If your pool surfaces already show signs of calcium buildup, proper cleaning methods can restore their appearance. For plaster surfaces, gently scrubbing with a pumice stone is an effective solution. For tile surfaces, using vinegar and a soft brush helps remove deposits without causing damage. Regular maintenance and cleaning prevent buildup from recurring and keep your pool looking pristine.
Common Questions about Hardness in Pool Water
Many pool owners wonder what causes calcium issues and how to address them effectively. Excess calcium often results from chemical imbalances or external factors like temperature changes and evaporation
- What causes calcium precipitation in pools?
Chemical imbalances, fluctuating temperatures, and evaporation are common culprits.
- How can I test calcium levels?
Most pool test kits measure calcium along with other critical parameters like pH and alkalinity.
- Is it possible to eliminate calcium completely?
No, calcium is essential for water balance. Strive to maintain levels within the recommended range.
- How do I prevent recurring calcium issues?
Adopt a consistent maintenance routine, use a sequestering agent, and ensure proper pH and alkalinity levels.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining the correct hardness in pool water is essential for the health of your pool, its structural components, and the enjoyment of its users. Balanced calcium hardness prevents both scaling and corrosion, ensuring a safe and visually appealing swimming environment. Regular testing, timely adjustments, and consistent chemical maintenance are key to achieving this balance.
By addressing calcium hardness proactively, you can avoid costly repairs and prolong the lifespan of your pool. When in doubt, consult a pool professional who can provide tailored advice to keep your pool in top condition for years to come.
Related Articles
Top 6 Shrimp Diseases in Aquaculture and Treatment
Shrimp diseases are a significant challenge in the aquaculture industry, affecting shrimp health, ...
What is Hardness in Pond Water and How Does it Affect My Fish?
Understanding the hardness of pond water is vital for maintaining a balanced and thriving aquatic ...
What is Nitrate and How Can We Manage It in Our Environment?
Nitrate is a vital compound found naturally in our environment and widely used in agriculture, ...
The Science of Water Hardness: How Does Water Hardness Affect My Home?
Water hardness is an important yet often overlooked aspect of water quality. Defined simply, water ...
How to Test Pond Water for Optimal Quality
Maintaining a healthy pond ecosystem requires consistent monitoring and management of water quality. ...
Understanding and Managing Nitrite in Pond Water
Nitrite in pond water is a critical topic for pond keepers, especially those with fish such as koi. ...