Aquaculture is a rapidly expanding industry and plays a vital role in providing a sustainable source of protein to meet the growing demand for seafood worldwide. As per the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), nearly 50% of the fish consumed globally comes from aquaculture, and its contribution to global fish production is expected to reach 53% by 2030. However, maintaining optimal water quality is critical for the success and sustainability of aquaculture operations. This article explores the importance of water quality in aquaculture and provides valuable insights on how to manage and maintain it effectively.
The Crucial Role of Water Quality in Aquaculture
In aquaculture, water quality is the most critical factor that determines the health and productivity of fish, shrimp, and other aquatic organisms. Unlike terrestrial animals, which rely on air to breathe, aquatic organisms live in water, making them highly sensitive to changes in their aquatic environment. All essential metabolic processes, such as feeding, digestion, excretion, and growth, occur in the water. Therefore, the water quality must be maintained at optimal levels to ensure that these processes occur efficiently, without stress or impairment to the aquatic species.
Water quality is particularly crucial in high-density stocking environments, where large populations of fish or shrimp are kept in confined spaces. Overcrowding can cause rapid deterioration of water quality due to increased waste products and reduced oxygen levels, resulting in adverse effects on the health and growth of the aquatic organisms. Regular monitoring of water quality parameters is therefore vital to prevent problems and maintain a healthy, productive aquaculture system.

The Crucial Role of Water Quality in Aquaculture
The Consequences of Poor Water Quality in Aquaculture
Poor water quality can have severe consequences on fish and shrimp health. Among the various water quality parameters, ammonia and dissolved oxygen levels are particularly critical. Ammonia, a toxic byproduct of fish excretion and waste feed, can cause significant stress, gill damage, and even mortality in high concentrations. It is one of the most dangerous substances for aquatic life, and its accumulation in water can lead to production losses that may go unexplained without proper water quality management.
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is equally important, as fish and shrimp rely on it to breathe. Insufficient oxygen levels can lead to respiratory distress, stress, and even death. Maintaining optimal oxygen levels is vital for the survival and growth of aquatic species. In intensive farming environments, where high stocking densities are common, the dissolved oxygen level can fluctuate significantly, increasing the stress on the organisms. Therefore, constant monitoring and timely adjustments are required to ensure that oxygen levels remain stable.
Overcrowding in aquaculture facilities can lead to the buildup of toxic nitrogenous compounds like ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates. These compounds are harmful to fish and shrimp, affecting their health, growth, and immune systems. Additionally, uneaten feed and waste materials, if not properly managed, contribute to the accumulation of these harmful compounds in the water, further deteriorating the water quality.

The Consequences of Poor Water Quality in Aquaculture
Optimizing Water Conditions for Aquaculture
To optimize water quality in aquaculture, several strategies can be employed. These strategies focus on maintaining a balance between nutrients, waste management, and proper fish nutrition.
1. Effective Feeding Practices
One of the key strategies to improve water quality is proper feeding practices. Overfeeding is a common problem in aquaculture, leading to excess nutrients and waste materials accumulating in the water. Uneaten feed contributes to the buildup of nitrogenous compounds like ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates, which can harm the aquatic organisms. To mitigate this, it is essential to feed fish and shrimp the right amount of food based on their size and species' nutritional needs.
Additionally, high-quality feed that meets the specific nutritional requirements of the cultured species can help improve their growth and reduce the amount of waste produced. By minimizing excess feed and ensuring that all nutrients are absorbed efficiently, the water quality will remain optimal for the health and growth of the aquatic species.
2. Waste Treatment and Filtration Processes
Aquaculture facilities, especially those that operate on a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS), require efficient waste management and filtration systems to ensure water quality is maintained. Mechanical filters can remove solid waste particles, while biofilters help in removing dissolved nitrogenous compounds from the water. These filtration systems can significantly reduce the buildup of harmful substances and improve the overall water quality in aquaculture tanks.
Regular maintenance and cleaning of filtration systems are crucial to ensure their efficiency. Without proper filtration, waste buildup can cause spikes in ammonia and other toxic substances, leading to poor water quality and stressing the aquatic species.
3. Monitoring and Testing
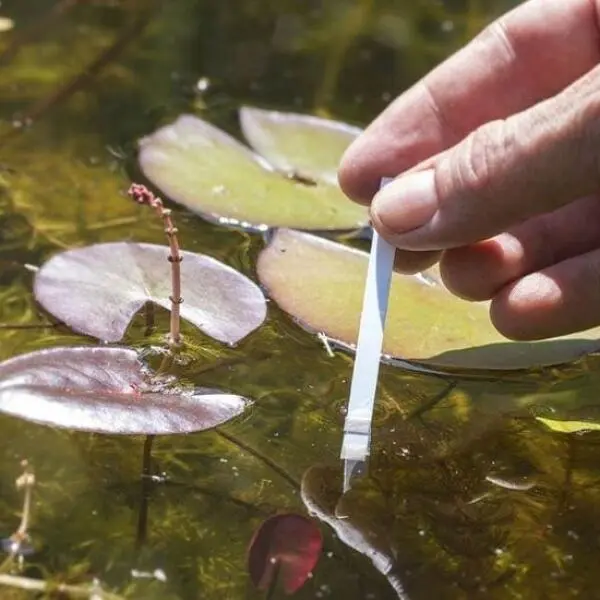
Regular monitoring and testing of water quality parameters, such as dissolved oxygen, ammonia, nitrites, pH, and temperature, are essential to ensure that water quality remains within the optimal range for the species being farmed. Test kits are available for measuring various water quality parameters, including ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, dissolved oxygen, and alkalinity. Regular testing allows farmers to detect potential problems early and take corrective actions before they impact the health of the aquatic organisms.
4. Promoting Natural Defenses
Adding specific nutrients and minerals to the water can help promote the natural defense systems of fish and shrimp, improving their health and resilience. Products like Aquate® are designed to enhance biomass production, boost immune systems, and encourage healthier populations of aquatic organisms. By providing essential minerals and additives, fish and shrimp are better equipped to handle stress, improve their digestion, and utilize nutrients more effectively.
Additionally, using yeast-based additives in the feed helps reduce waste and minimize the pollution generated in the farming system, further improving water quality.
5. Reducing Ammonia Toxicity
Ammonia toxicity is one of the most significant concerns in aquaculture. To combat this, natural solutions can be employed to reduce ammonia levels without harmful chemicals. One such product is De-Odorase®, which contains yucca plant extract. Yucca extract binds to ammonia, preventing its accumulation and reducing its harmful effects on aquatic species. This product can be especially beneficial in ponds with high pH levels, where ammonia tends to accumulate rapidly.
6. Regular Water Exchanges
In systems where water is not recycled, such as open systems, regular water exchanges are crucial to maintain water quality. Water exchanges help remove excess nutrients, organic matter, and nitrogenous compounds from the system, reducing the risk of disease outbreaks and maintaining a healthy environment for the fish and shrimp. In recirculating systems, while water is filtered and treated, periodic water exchanges are still necessary to ensure that the water remains fresh and free from contaminants.
7. Pond Management
In pond farming, the pH level of the water is a critical factor that affects the buildup of ammonia and nitrites. Maintaining the pH within the optimal range for the species being farmed is essential for reducing the risk of ammonia toxicity. Additionally, the rate of nitrogen assimilation by bacteria and phytoplankton must be closely monitored to ensure that ammonia and nitrites are effectively removed from the system. When high-protein feeds are used, it is important to balance feeding rates with the capacity of the system to assimilate nitrogen compounds.
Selecting a Suitable Water Resource
Choosing the right water source is an essential step in ensuring the long-term success of any aquaculture operation. Water quality should be thoroughly tested to check for contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, or excess nutrients. An ideal water source should be uncontaminated, have a consistent supply, and meet the water quantity requirements for the farm. Springs and wells are often the best sources for aquaculture because they typically have fewer contaminants compared to other sources, such as rivers or municipal water.
Water tests should be conducted regularly to check for various contaminants and water quality parameters. This ensures that any issues with the water source are detected early, allowing for timely corrective measures.

Selecting a suitable water resource
Conclusion
Water quality is the backbone of a healthy and productive aquaculture system. By monitoring and managing key water quality parameters, such as dissolved oxygen, ammonia, pH, and temperature, aquaculture operations can maintain a stable environment conducive to the growth and health of aquatic organisms. The implementation of strategies such as efficient feeding practices, waste management, and natural defenses can help optimize water quality and ensure sustainable production. By investing in proper water quality management, aquaculture farmers can enhance productivity, reduce environmental impact, and contribute to the growing demand for sustainable seafood worldwide.
Related Articles
What Causes Ammonia Leaks? How to Handle Them
Ammonia is a critical component in various industrial processes, particularly in refrigeration ...
How Ammonia Fuel Works and Its Role in Renewable Energy
With the growing demand for alternatives, ammonia fuel is emerging as a promising standout in the ...
The Role of Algae in Aquatic Environments
Algae play an essential role in maintaining the balance and health of aquatic ecosystems. Often ...
The Impact of Heavy Metals on Aquaculture Water: Challenges and Solutions
Aquaculture water is an indispensable resource in ensuring the health and sustainability of aquatic ...
What is Pond Water Alkalinity and Why Does it Matter?
As a pond owner, ensuring the health and well-being of your Koi and Goldfish requires a keen ...
What Happens When Alkalinity in Pool is Too High or Too Low?
Has your pool water turned cloudy or developed unsightly scaling on its surfaces? These are common ...