Antibiotics in farming are important in modern, supporting livestock health and ensuring efficient food production. However, their widespread use has raised concerns about antibiotic resistance, environmental impact, and food safety. In this article, we will explore how antibiotics are used in farming, their pros and cons, and potential solutions for more sustainable agricultural practices.
What Are Antibiotics in Farming?
Antibiotics are medications used to treat bacterial infections in both humans and animals. In farming, antibiotics serve three main purposes:
- Treatment of Illness: Antibiotics treat bacterial infections in livestock, preventing outbreaks that could devastate herds or flocks.
- Disease Prevention: In some cases, antibiotics are administered proactively to healthy animals to prevent diseases in high-risk environments.
- Growth Promotion: Low doses of antibiotics are sometimes added to animal feed to promote growth, improve feed efficiency, and increase meat production. While this way of using antibiotics is banned in many countries, it persists in some regions.
The widespread adoption of antibiotics in farming stems from the need to maintain animal health, increase farm productivity, and meet growing global demands for food.
The Common of Antibiotics in Farming
The use of antibiotics in farming is particularly significant in large-scale livestock operations. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 70% of the world's antibiotics are used in animals, not humans.
- In industrial livestock farming, antibiotics help animals gain weight faster by improving digestion and reducing bacterial infections.
- In aquaculture, antibiotics are used to prevent and treat infections in fish and shrimp farms.
Regions with high meat consumption, such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, see the most extensive use of antibiotics in farming.
Advantages of Antibiotic Use in Farming
Antibiotics provide several key benefits in modern agriculture:
Improved Animal Health
Using antibiotics in farming prevents and treats infectious diseases that can spread rapidly in large herds or flocks. Farmers reduce economic losses caused by illness and death by maintaining healthier animals.
Increased Food Production
Antibiotics enhance growth rates, helping animals convert feed into body weight more efficiently. This leads to higher yields of meat, milk, and eggs, enabling farmers to meet consumer demand.
Cost-Effectiveness
Healthier animals require fewer resources, such as food and medical care, which makes antibiotic use economically beneficial for large-scale farming operations.
Food Security
By reducing the spread of diseases, antibiotics help stabilize food supply chains, ensuring the availability and affordability of animal-based products.
The Risks and Challenges of Antibiotic Use in Farming
While antibiotics offer substantial benefits, their excessive and inappropriate use in farming raises serious concerns:
1. Antibiotic Resistance
One of the most significant risks of using antibiotics in farming is the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Over time, bacteria exposed to antibiotics adapt and evolve, rendering these medications ineffective.
- Resistant bacteria can transfer to humans through contaminated meat or direct contact with animals.
- Common infections once treatable with antibiotics may become more difficult and expensive to manage.
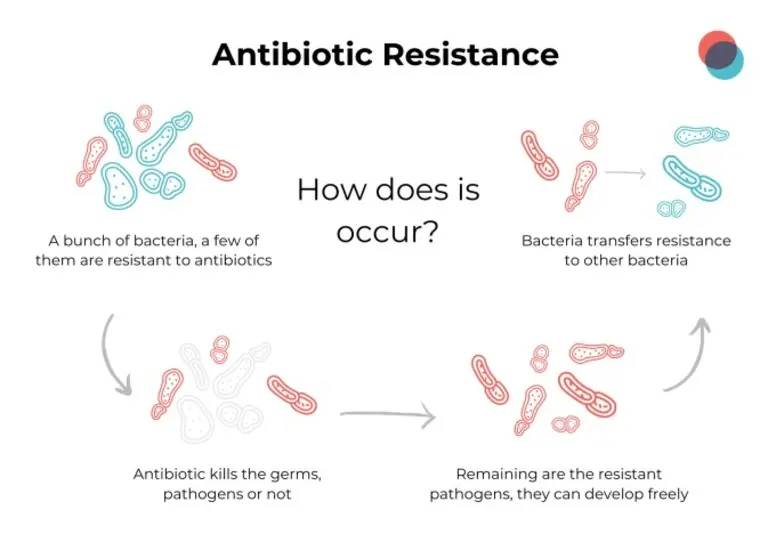
The World Health Organization (WHO) has labeled antibiotic resistance as a global health crisis linked to farming practices.
2. Residues in Food Products
If not properly monitored, animal antibiotics can leave residues in meat, milk, and eggs. Long-term exposure to these residues may pose health risks, such as allergic reactions or antibiotic resistance.
Regulations, such as withdrawal periods before slaughter, aim to minimize residues, but improper use in unregulated markets remains a concern.
3. Environmental Impact
Animal waste is an instance in which antibiotics can get into the environment. When manure is used as fertilizer, antibiotics and resistant bacteria may contaminate soil, water, and crops. This can disrupt ecosystems and further spread resistance.
4. Public Health Concerns
Humans exposed to resistant bacteria may experience more severe infections, longer hospital stays, and increased mortality rates. Diseases like E. coli or Salmonella, linked to antibiotic resistance, highlight the impact of farming practices on public health.
Limitations on the Use of Antibiotics in Farming
Recognizing the risks, many countries and organizations are taking steps to limit the use of antibiotics in farming:
- Bans on Growth Promoters: The European Union banned antibiotics as growth promoters in 2006, followed by similar restrictions in the United States and other regions.
- Improved Regulations: Farmers are required to obtain veterinary prescriptions before using antibiotics, ensuring responsible use.
- Promotion of Alternatives: Farmers are encouraged to adopt alternatives, such as probiotics, vaccines, and better hygiene practices, to reduce reliance on antibiotics.
- Global Action Plans: The World Health Organization (WHO) and other agencies are working to combat antimicrobial resistance through global strategies and collaborations.
Solutions to Antibiotics in Farming
To reduce reliance on antibiotics, farmers and researchers are exploring alternative methods to maintain livestock health:
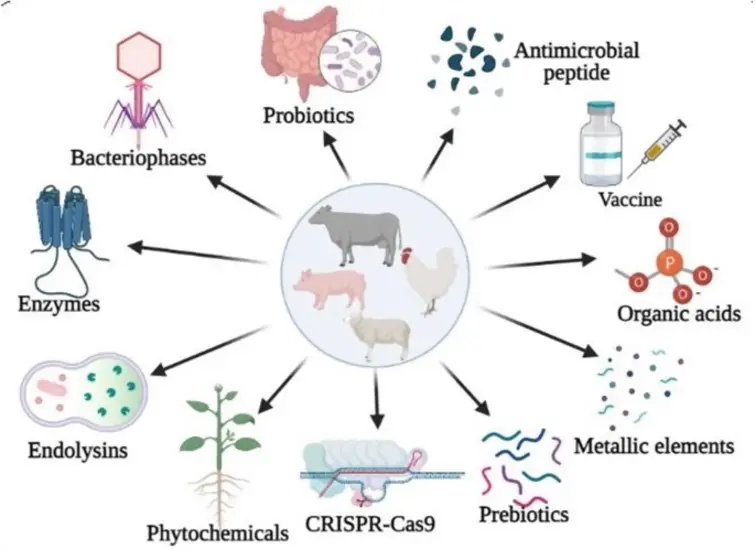
- Improved Hygiene and Biosecurity: Maintaining clean and safe living conditions reduces the risk of disease outbreaks and minimizes the need for antibiotics.
- Vaccines: Vaccines protect animals from specific diseases, reducing the likelihood of infections that require antibiotic treatment.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: These supplements promote healthy gut bacteria, enhance the immune system, and reduce the need for antibiotics.
- Selective Breeding: Breeding livestock for disease resistance can decrease infection susceptibility.
- Natural Feed Additives: Plant-based feed additives, such as essential oils and herbs, are being studied for their antimicrobial properties.
How Antibiotics Affect Society
The connection between antibiotics in farming and public health is a growing concern:
Antibiotic-resistant diseases
- Resistant bacteria from farms can infect humans, leading to harder to treat illnesses.
- Common examples include multidrug-resistant Salmonella and E. coli.
Strain on Healthcare
- Antibiotic resistance increases healthcare costs, hospital stays, and mortality rates.
Collaborative Responsibility
- Addressing antibiotic resistance requires cooperation between farmers, healthcare providers, policymakers, and consumers.
Steps Farmers Can Take to Addressing Antibiotic Use
Farmers play a crucial role in reducing antibiotic use while maintaining productivity:
1. Implementing Best Practices: Use antibiotics only when prescribed by a veterinarian. Follow the directions and the suggested dosage.
2. Monitoring and Record-Keeping: Track antibiotic usage to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
3. Investing in Animal Health: Provide balanced nutrition, regular vaccinations, and stress-free environments to boost immunity.
4. Collaborating with Experts: Work with veterinarians and agricultural advisors to develop effective health management plans.
Conclusion
The use of antibiotics in farming has undeniably revolutionized agriculture by improving animal health and boosting food production. However, the overuse and misuse of these medications pose serious threats to public health, the environment, and long-term food safety.
Tackling these challenges requires a collective effort from farmers, policymakers, scientists, and consumers. By adopting sustainable practices, exploring alternatives, and raising awareness, we can ensure a healthier future for both humans and animals.
Related Articles
The Truth About Alkaline Water: Is It Worth It?
Alkalinity water is an increasingly popular topic in health and wellness discussions. As consumers ...
What Happens When Alkalinity in Pool is Too High or Too Low?
Has your pool water turned cloudy or developed unsightly scaling on its surfaces? These are common ...
What is Pond Water Alkalinity and Why Does it Matter?
As a pond owner, ensuring the health and well-being of your Koi and Goldfish requires a keen ...
What Is an Alkaline Solution?
An alkaline solution is a liquid mixture formed when an alkali dissolves in water, creating a ...
How Can I Measure and Maintain Proper Alkalinity Levels?
Alkalinity is a crucial property of water that influences its ability to maintain a stable pH ...
What Factors are Measured in Water Quality Indices?
Water quality indices (WQIs) are essential tools for assessing the health of aquatic ecosystems and ...






