Calcium hypochlorite , with the molecular formula Ca(ClO)2, is a widely used chemical compound known for its powerful oxidizing properties and its extensive applications in various industries. This article delves into the comprehensive understanding of this chemical, covering its physical and chemical properties, manufacturing processes, safety considerations, and its diverse applications in water treatment, disinfection, and beyond.
Properties of Calcium Hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is known for its unique physical and chemical characteristics, which contribute to its diverse range of applications.
Physical Properties
This is a chemical compound with the molecular formula Ca(ClO)2 and a molecular weight of 142.974 g/mol. Its CAS number is 7778-54-3 It has a specific gravity of 1.21 g/cm³, making it a dense material. This compound is known for its powerful oxidizing properties, which enable it to effectively sterilize and disinfect various applications.
Chemical Structure
The structure of calcium hypochlorite has been refined using X-ray powder diffraction data, revealing an orthorhombic crystal system with the space group Ccca (Ccce) and Z = 4. The structure consists of separate layers parallel to the ac plane, where calcium cations are coordinated by chlorite anions, and the oxygen atoms form almost ideal square antiprisms.

What is Calcium Hypochlorite?
Manufacturing Processes
Calcium hypochlorite is manufactured through two main processes: the "calcium process" and the "sodium process." Both methods involve the reaction of chlorine gas with either calcium hydroxide or sodium hypochlorite.
In the calcium process, the reaction is as follows:
2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 ⇒ Ca(ClO)2 + CaCl2 + 2H2O
The product of this process is a mixture of calcium hypochlorite, calcium chloride, and calcium chloride hypochlorite, commonly known as “bleaching powder.”
In the alternative sodium process, chlorine gas is reacted with calcium hydroxide:
Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 ⇒ Ca(ClO)2 + 2HCl
In this method, the excess HCl is neutralized by the excess Ca(OH)2 to form calcium chloride, resulting in a more "neutral" and stable product compared to other manufacturing methods.
The products from these two methods are nearly identical, and the resulting compound is often referred to as "bleaching powder".
The calcium process involves the direct reaction of chlorine gas with calcium hydroxide, producing calcium hypochlorite and calcium chloride as the main products. This method is relatively straightforward and has been widely used in the manufacturing of this chemical.
In contrast, the sodium process utilizes sodium hypochlorite as the starting material, which then reacts with calcium hydroxide to form calcium hypochlorite. This process can be advantageous in situations where sodium hypochlorite is more readily available or economical. The final products from both methods are similar in terms of their chemical composition and properties.
It's worth noting that the manufacturing of this chemical requires careful control and safety measures due to the reactive nature of the starting materials and the potential for the release of hazardous gases during the production process.
Safety Considerations
Calcium hypochlorite is a powerful oxidizing agent, and its hazardous properties require careful handling and storage. The following sections outline the key safety considerations for this compound.

Be careful when using Calcium hypochlorite
Explosive Hazards
Calcium hypochlorite can react violently in the presence of water, heat, or when combined with certain organic materials, such as carbon compounds, oils, hydrocarbons, and alcohols. These reactions can lead to explosive situations and should be avoided. Specific storage and handling methods have been developed for large-scale users to mitigate these risks.
Toxic Gas Release
When heated or in contact with acids, this chemical can release highly toxic gaseous chlorine. This poses a significant safety hazard and must be considered when handling or storing the compound.
Incompatible Substances
Calcium hypochlorite should be kept away from incompatible substances, such as urea (which can form highly explosive NCl3), organic sulfur compounds, and metals like iron oxide, which can catalyze the oxygen-evolving decomposition of the oxidant.
Storage and Handling
Bleaching powder, the commercial form of calcium hypochlorite, is generally supplied to the public as a 3% solution. Specific methods of storage for large users (such as textile manufacturers) have been developed to ensure the stability and safe handling of the compound.
When large quantities become necessary upon short notice, specialized equipment and storage facilities become economical. This is due to the need to contain the solution until it is used, as this is a strong oxidant that may react with vigor in combination with carbon compounds, and the combination with finely divided carbon particles forms an explosive mixture.
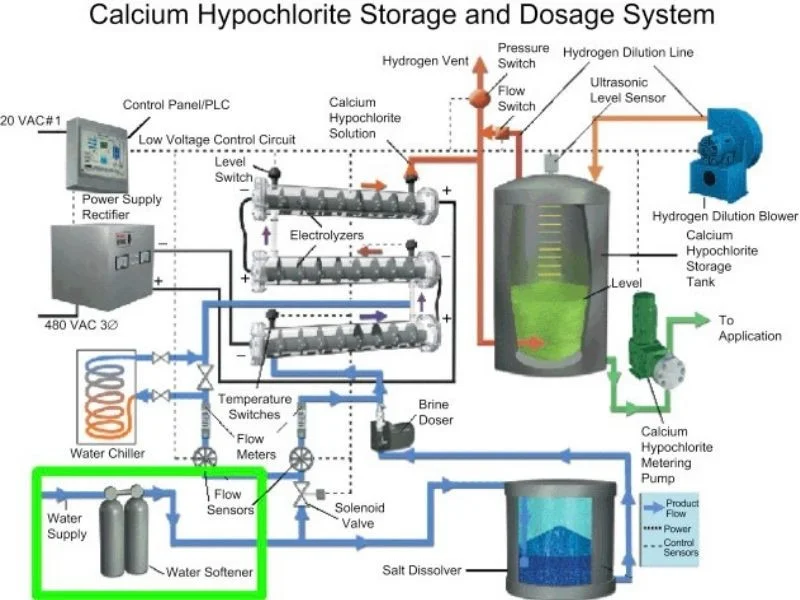
Calcium hypochlorite storage system
Uses of Calcium Hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite has a wide range of applications, including:
Treating industrial wastewater
The oxidizing properties of calcium hypochlorite make it an effective agent for treating industrial wastewater. The compound can help remove organic matter, and disinfect, and neutralize the pH of wastewater, making it suitable for various industrial processes and environmental protection.
Sanitation and Cleaning
Calcium hypochlorite is widely used for disinfection and sanitization purposes. It is commonly employed in swimming pools, drinking water treatment, vegetable cleaning, and fishpond maintenance to kill microorganisms and maintain hygienic conditions.
Household Sanitation
Calcium hypochlorite plays a crucial role in epidemic prevention and the maintenance of sanitation in household facilities. Its disinfecting properties make it valuable in controlling the spread of infectious diseases and maintaining overall cleanliness in various settings.
Textile Industry
The development of bleaching powder by Scottish chemist Charles Tennant revolutionized the textile industry by dramatically reducing the time required for the traditional bleaching process. Calcium hypochlorite has been used for bleaching cotton, hemp, fibers, pulp, and starch, significantly improving the efficiency and effectiveness of textile manufacturing.
Other Uses
Calcium hypochlorite has also been proposed as a solid fire extinguisher due to its endothermic phase transition and chlorine stability properties. The compound's ability to release water and chlorine in an endothermic reaction can help quench dangerous fires and reduce the potential for conflagration.

Treating industrial wastewater
Conclusion
Calcium hypochlorite is a versatile and essential chemical compound with a wide range of applications, from water treatment and disinfection to textile bleaching and fire extinguishing. Its unique properties, manufacturing processes, and safety considerations make it a crucial player in various industries and applications. As the demand for effective and sustainable disinfection and sanitization solutions continues to grow, the importance of this chemical in maintaining public health and environmental well-being cannot be overstated.
Related Articles
Why Does Tap Water Smell Like Chlorine and How to Remove It?
Tap water often has a distinct chlorine smell , which can be unpleasant and concerning for many ...
How to mix and use chlorine powder 70% to treat water
How to mix or use chlorine powder 70% is always the issue that receives great attention from ...
Difference between chlorine powder and chlorine pellets in wastewater and swimming pool water treatment
In mentioning kinds of chemicals, chlorine powder and chlorine pellets are the two most popular ...
Unveiling Liquid Chlorine: Uses and Safety
Liquid chlorine , also known as chlorinated water or hypochlorite solution, is a versatile chemical ...
Top 3 Applications of Chlorine Powder
Chlorine powder , also known as calcium hypochlorite (Ca(OCl)2), is a widely used disinfectant ...
The Ultimate Guide to Chlorine Powder for Pool Water Treatment
Maintaining a clean pool is crucial for the health and enjoyment of swimmers. One of the most ...






