In the realm of water quality management, alum treatment has emerged as a highly effective method for addressing nutrient pollution in lakes and ponds. This comprehensive guide will explore the benefits, applications, and considerations of using alum (aluminum sulfate) to improve water quality in freshwater ecosystems.
Understanding the Need for Alum Treatment
Healthy aquatic ecosystems require a delicate balance of nutrients to support the food chain and maintain water quality. However, human activities such as urban development, land clearing, pollution, and intensive agriculture can disrupt this balance by introducing excessive nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, into our freshwater resources.
When lakes and ponds suffer from nutrient overload, they may exhibit several problematic symptoms:
- Poor water clarity
- Nuisance algae and vegetation growth
- Unpleasant shoreline odors
- Gradual loss of water depth
- Fish kills due to oxygen depletion
These issues not only impact the aesthetic and recreational value of water bodies but also pose significant ecological challenges. This is where alum treatment comes into play as a powerful tool for lake and pond restoration.
The need for alum treatment
The Scientific Principles of Alum Treatment
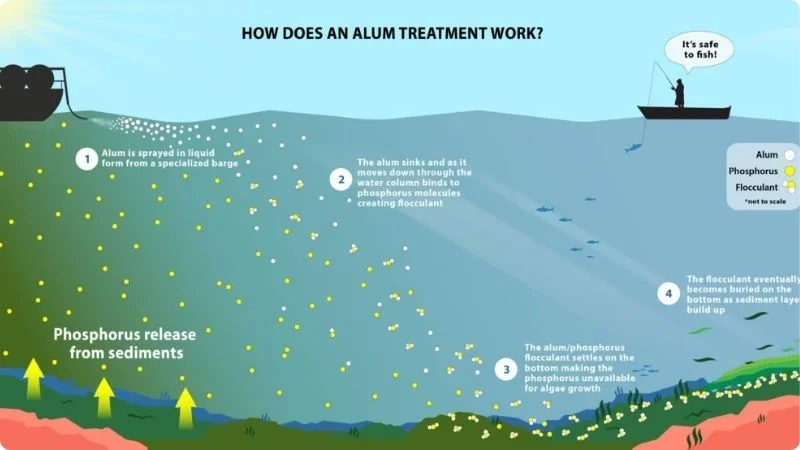
Alum, or aluminum sulfate (Al2(SO4)3 · 14 H2O), has been used in water purification and wastewater treatment for centuries. In recent decades, it has gained popularity as an effective method for lake restoration. But how does it work?
When alum is introduced to water, it undergoes a series of chemical reactions:
- Aluminum ions are formed and hydrated: Al+3 + 6 H2O ⇄ Al (H2O)63+
- Through hydrolysis steps, hydrogen ions are released, and aluminum hydroxide is formed: Al3+ + H2O ⇄ intermediate reactions ⇄ Al(OH)3(s) + H+
The resulting aluminum hydroxide creates a flocculent material, known as "floc," which has a high capacity to adsorb phosphates. This floc settles to the bottom of the lake or pond, forming a barrier that helps prevent the release of phosphorus from the sediment.
The Alum Treatment Process
Alum treatment for lakes and ponds typically involves the following steps:
- Assessment: Water quality experts evaluate the nutrient levels and overall condition of the water body to determine if alum treatment is appropriate.
- Planning: A customized treatment plan is developed, considering factors such as lake size, depth, and phosphorus concentrations.
- Application: Alum is injected several feet below the water's surface using specialized equipment. The treatment is usually conducted in the late fall or early spring over a period of 7-10 days.
- Floc Formation: Upon contact with water, the alum forms aluminum hydroxide floc, which begins to bind with excess phosphorus in the water column.
- Settling: The floc settles to the bottom of the lake, creating a protective layer over the sediment that continues to bind with phosphorus as it is released from the bottom.
- Monitoring: Water quality is closely monitored following the treatment to assess its effectiveness and ensure optimal results.

The Alum Treatment Process
Benefits of Alum Treatment
Alum treatment offers several significant advantages for lake and pond management:
- Rapid Improvement: Water clarity can increase dramatically within hours of treatment, with reductions in algae noticeable within one year.
- Long-lasting Effects: In lakes with significant internal phosphorus loading, alum treatments can maintain water quality improvements for 15 to 20 years.
- Targeted Nutrient Control: Alum specifically targets excess phosphorus, a key driver of algal blooms and water quality issues.
- Minimal Ecological Impact: When applied correctly, alum treatment has minimal impact on aquatic plants and animals.
- Cost-effective: Compared to other lake restoration techniques, alum treatment can be a cost-effective solution for long-term water quality improvement.
Safety Considerations
One of the primary concerns surrounding alum treatment is its safety for both humans and aquatic life. However, extensive research and decades of use have demonstrated that alum is a safe option when applied correctly:
- Human Health: There is no evidence to suggest that aluminum in treated water poses a health threat. In fact, aluminum hydroxide is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter antacids.
- Aquatic Life: The aluminum hydroxide floc is harmless to aquatic plants and animals when it settles to the lake bottom.
- pH Management: To prevent potential toxicity issues related to pH changes, many treatments now use buffered alum, which helps control pH levels within acceptable ranges.
- Drinking Water: Alum treatments in lakes and reservoirs used for drinking water supplies do not pose a risk, as water treatment facilities often use alum as a clarifier in their purification processes.
When is Alum Treatment Appropriate?
While alum treatment is highly effective, it's essential to consider it as part of a comprehensive lake management strategy. Here are some situations where alum treatment may be particularly appropriate:
- High Internal Phosphorus Loading: Lakes with significant phosphorus release from sediments can benefit greatly from alum treatment.
- Limited External Nutrient Sources: When external phosphorus inputs have been addressed, but water quality issues persist due to internal loading.
- Rapid Improvement Needed: In cases where immediate water quality improvement is required for ecological or recreational reasons.
- Complement to Watershed Management: Alum treatment can be used in conjunction with watershed management practices for more comprehensive results.
- Cost-effective Alternative: When other phosphorus control methods are prohibitively expensive or impractical.

When is Alum Treatment Appropriate?
Balancing Alum Treatment with Watershed Management
While alum treatment is highly effective at addressing internal phosphorus loading, it's crucial to remember that it treats the symptoms rather than the root cause of nutrient pollution. A balanced approach that combines alum treatment with watershed management practices is often the most effective strategy for long-term lake and pond health.
The balanced system is comprised of the following key elements:
- Reducing External Nutrient Inputs: Implementing best management practices in the watershed to minimize nutrient runoff from agriculture, urban areas, and other sources.
- Erosion Control: Stabilizing shorelines and implementing measures to reduce sediment input into the water body.
- Stormwater Management: Improving stormwater infrastructure to reduce the influx of nutrients during rain events.
- Public Education: Engaging local communities in efforts to reduce nutrient pollution through landscaping practices, proper septic system maintenance, and responsible fertilizer use.
- Monitoring and Adaptive Management: Regularly assessing water quality and adjusting management strategies as needed.
Conclusion
Alum treatment has proven to be a powerful tool in the fight against nutrient pollution in lakes and ponds. Its ability to rapidly improve water clarity, control algal blooms, and provide long-lasting phosphorus control makes it an attractive option for many water resource managers. However, it's essential to approach alum treatment as part of a comprehensive lake management strategy that addresses both internal and external nutrient sources.
By combining alum treatment with watershed management practices and ongoing monitoring, we can work towards healthier, clearer, and more resilient aquatic ecosystems. As we continue to face challenges related to water quality and climate change, innovative solutions like alum treatment will play a crucial role in preserving our valuable freshwater resources for future generations.
Related Articles
How Pool Flocculant Works and When to Use It
Keeping pool water clean and clear is a priority but sometimes regular maintenance isn’t enough to ...
Alum Water: A Simple Solution for Clean Water and More
Alum water , a solution created by dissolving alum in water, has been used for centuries as a ...
What You Need to Know Alum Treatment for Pools
Alum treatment , also known as aluminum sulfate treatment, is a widely used method for improving ...
Clear Water in a Flash: The Magic of Pool Flocculant
Maintaining a pristine swimming pool can be challenging, especially when dealing with persistent ...
A Look at Bacterial Life: The Good, the Bad, and the Tiny
Bacteria , the microscopic organisms that have inhabited Earth for approximately 4 billion years, ...
The Role of Bacteria in Pond Health
Clear, healthy pond water isn't just a matter of luck – it's the result of countless microscopic ...